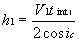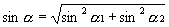Critical and head waves - critical angle ic intersects and travels
at 90o. If they are more oblique they are reflected.
so: sinic/V1 = sin90o/V2
==> sinic = V1/V2(sin90o) =
V1/V2 ==> qc = sin-1(V1/
V2)
Huygen's principle: each point on a wave front acts as a new source for waves.
Diffraction - bending of waves into shadows. Radial scattering of incident seismic
energy.
- Edges of faulted layers
- Small isolated object
e.g., boulder in a homogeneous layer
difficult to identify
Fermat's Principle - a ray that reaches a particular point does so in a
minimum time.
Head Waves:
sinihead = V1/V2 = sinic
So head waves are the same as the critical refraction. The refracted rays are than the
measurements of the time to receivers for head waves.
Travel time diagram
- head wave
- direct wave - travels just below the interface
- reflected waves
The direct wave is measured by 1/V1
The refracted wave is measured by 1/V2
The refracted wave starts at the criticak distance. This is where the reflection and
refraction coincide.

=>
Reflected ray: 2hi/V1 - never first arrivals
First arrivals for near surface distances are direct rays whereas beyond a certain
distance (the crossover distance) are the fastest.
Source - shot point
Locating the first arrival is called picking
The calculation between the picks and distance to source will yield velocities
To calculate the depth of an interface can use:

 =>
=> 
For Muiltiple Layers:

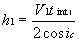






This continues for each interface.
Dipping Interfaces:
Flat Layers vs. Dipping Layers
- The slope of the refraction line is less steep up dip, steeper down dip
- The intercept is less at the up-dip than down-dip end
- The slopes for direct rays (first sections on the travel time plot) are
unchanged
The true dip
- Shooting along strike gives is a parrallel view. The structure appears horizontal.
- Obliquely the dip will be too low
- True dip can be obtained by using two line perpendicular to eachother
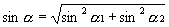

where q is the angle between the dip direction
and the seismic line from a
Seismic Velocity
- Generally velocity increases with depth
- The best measurement is in boreholes
- Weathering of rocks will lower the velocity of rocks
Hidden Layers
- Thin layer of strata
- Low Velocity Layer (LVL)
A seismic interface is not necessarily a geologic boundary. Some rocks may be
to similar in type. So velocity would not seperate these interfaces out.
Survey
- Various scales
- Need:
- Source
- line of receivers
- Timing
- Hammer seismics
- strike a plate on the ground with a hammer, a switch closes, and the
recording unit starts.
- Distance of profile is dependent on:
- the system
- size of the hammer
- rocks
- noise - to reduce noise you can bury the cables and/or lay the cable
flat
- Can stack data by hitting the hammer several times in the same location
- typically goes ~ 100m distance for such profiles
- shallow surveys rule of thumb:
10x the depth to interface in 100 m line = recording depth of 10 m
- Explosion seismics
- want energy to go down not up, so bury the charges
- drill holes are expensive, the best holes are below the water table for
better coupling. can try to take advantage of a water body as well. Shooting
in water is cheaper as well.
- this type of survey is just a hammer survey on steriods
- Land surveying in general
Have to think about station spacing. Two far apart and you may miss varying
layers.
- Marine seismics
- use explosives, but most of the time airguns
- receivers are called hydrophones, measure the pressure changes
- shooting and receiving take place concurrently so several lines are
acquired. Boat time is very expensive.
- large explosives may be used for deep surveys
- Can have 2 ships out for reversals
- Sonobouys may be left out to record
- OBS sit at the bottom like land surveying. can get 3-component data this
way.
Undulating interfaces delay times
- Some surfaces may undulate
- topography
- basin/bedrock contacts
- moho
- Delay times:

- The deplay time is easiest calculated at the receiver:


can get tf,tr, and ttotal from the travel time
plot.
- The depth can be deduced:

Have to find V1 and V2 than you can determine the intercept time.
Plus-Minus Method
- plot 2 additional lines on the travel time curve
tf + tr
tf - tr
- slope is 2/V2 for tf - tr; so can get V2
- calculate V1 from the direct arrivals
- So ttotal for each receiver is subtracted from tf +
tr and then halfed (equation 6.11)
- then use eq. 6.12 to get depth of interface
- only used for part of the the profiles, has to be long,
typically only used for the first interface, not so good is the dip >10o
Ray tracing and synthetics
- have previously described inverse methods for interpretating refraction data
- forward modelling or ray tracing
- Using Snell's law
- can vary velocities
- point to fit the observed and calculated arrvials
- Can calculate amplitude
comparing synthetic with original data
- Can detect faults if the travel times are offset
Fan shooting - simple tomography
- shooting in a fan of receivers
- increases coverage area
Return to the Lectures Page
Return to the Class Page





 =>
=>